Informational Considerations

Informational considerations are those aspects of the human, information, and physical dimensions that affect how humans and automated systems derive meaning from, use, act upon, and are impacted by information (FM 3-0).
Information Capabilities

In addition to planning all operations to benefit from the inherent informational aspects of physical power and influence relevant actors, the joint force commander (JFC) also has additional means with which to leverage information in support of objectives. Leveraging information involves the generation and use of information through tasks to inform relevant actors; influence relevant actors; and/or attack information, information systems, and information networks.
Operations in the Information Environment (OIE)

Operations in the information environment (OIE) are military actions involving the integrated employment of multiple information forces to affect drivers of behavior by informing audiences; influencing foreign relevant actors; attacking and exploiting relevant actor information, information networks, and information systems; and by protecting friendly information, information networks, and information systems...
Informational Power
Power—the capacity or ability to direct or influence the behavior of others—has many forms. Informational power is an ability to use information to support achievement of objectivities and create information advantages.
Information Activities

Within the information advantage framework, Army forces integrate all relevant military capabilities through the execution of five information activities (enable, protect, inform, influence, and attack).
Information Advantage Framework

The information advantage framework presents a framework for creating and exploiting information advantages. Within this framework, Army forces integrate all relevant military capabilities through the execution of five information activities (enable, protect, inform, influence, and attack).
Information Advantage

An information advantage is a condition when a force holds the initiative in terms of situational understanding, decision making, and relevant actor behavior. There are several forms of information advantage.
NEW! INFO2 SMARTbook: Information Advantage

INFO2 SMARTbook: Information Advantage (Activities, Tasks & Capabilities) is the second edition of our INFO SMARTbook, completely updated for 2024 to include ADP 3-13, Information (Nov '23) and JP 3-04, Information in Joint Operations (Sep '22)...
Armed Conflict

Armed conflict occurs when a state or non-state actor uses lethal force as the primary means to satisfy its interests. Armed conflict can range from irregular warfare to conventional warfare and combinations of both...
Crisis Operations

A crisis is an emerging incident or situation involving a possible threat to the United States, its citizens, military forces, or vital interests that develops rapidly and creates a condition of such diplomatic, economic, or military importance that commitment of military forces and resources is contemplated to achieve national and/or strategic objectives...
Competition Below Armed Conflict

Competition below armed conflict exists when two or more state or non-state adversaries have incompatible interests, but neither seeks armed conflict...
Army Strategic Contexts
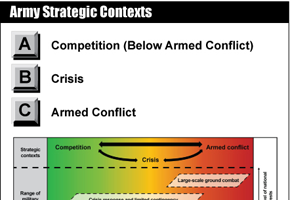
The Army strategic contexts generally correspond to the joint competition continuum and the requirements of joint campaigns. Army doctrine adds crisis to account for the unique challenges facing ground forces that often characterize transition between competition and armed conflict...
Consolidate Gains

Army commanders must exploit successful operations by continuously consolidating gains during competition, crisis, and armed conflict. Consolidate gains are activities to make enduring any initial operational success and to set the conditions for a sustainable security environment, allowing for a transition of control to other legitimate authorities...
Relative Advantages

A relative advantage is a location or condition, in any domain, relative to an adversary or enemy that provides an opportunity to progress towards or achieve an objective. Relative advantages are characterized as human, information, or physical, and they complement each other...
Competition Continuum
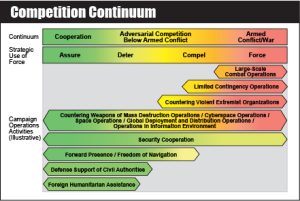
The four strategic uses of the military instrument of national power- assurance; both forms of coercion, deterrence and compellence; and forcible action - are implemented through campaigns, operations, and activities that vary in purpose, scale, risk, and intensity, and occur across a competition continuum...
Multidomain Operations

Multidomain operations are the combined arms employment of joint and Army capabilities to create and exploit relative advantages that achieve objectives, defeat enemy forces, and consolidate gains on behalf of joint force commanders...
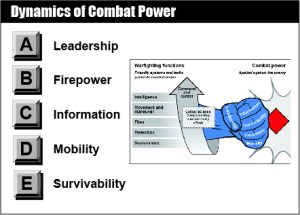
Dynamics of Combat Power

Combat power is the total means of destructive and disruptive force that a military unit/formation can apply against an enemy at a given time (JP 3-0). It is the ability to fight. The complementary and reinforcing effects that result from synchronized operations yield a powerful blow that overwhelms enemy forces and creates friendly momentum. Army forces deliver that blow through a combination of five dynamics...
NEW! JFODS6: The Joint Forces Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook, 6th Ed.

JFODS6 is the sixth revised edition of The Joint Forces Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook. JFODS6 is completely updated for 2023 with new/updated material from the latest editions of JP 3-0 Joint Campaigns and Operations (Jun ‘22), JP 5-0 Joint Planning (Dec ‘20)...
Rapid Decision-Making and Synchronization Process (RDSP)
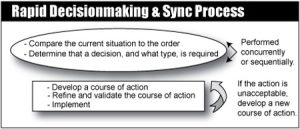
The rapid decision-making and synchronization process (RDSP) is a technique that commanders and their staffs commonly use during execution. While identified here with a specific name and method, the approach is not new; its use in the Army is well established and tested...
Troop Leading Procedures (TLP)
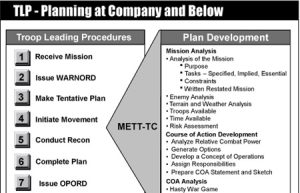
Troop leading procedures (TLPs) extend the military decisionmaking process (MDMP) to the small-unit level. The MDMP and TLP are similar but not identical...
Army Design Methodology (ADM)
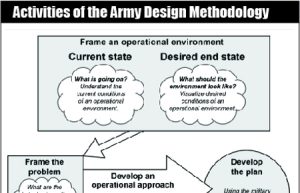
Army design methodology (ADM) is a methodology for applying critical and creative thinking to understand, visualize, and describe problems and approaches to solving them. It entails framing an operational environment (OE), framing problems, and developing an operational approach to solve or manage identified problems...
NEW! BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed.

BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed. is completely updated for 2023 to include FM 5-0 w/C1, Planning and Orders Production (2022); FM 6-0, Commander and Staff Organization and Operations (2022), FMs 1-02.1/.2, Military Terms & Symbols (2022); and more!
Leader Competencies

The core leader competencies are actions that the Army expects leaders to do: lead, develop, and achieve. Competencies provide an enduring, clear, and consistent way of conveying expectations for Army leaders. The core competencies are universal for all Army leaders.
Leader Attributes

Attributes are characteristics internal to a leader. These affect how an individual behaves, thinks, and learns within certain conditions. Strong character, solid presence, and keen intellect enable individuals to perform the core leader competencies with greater effect.
Leadership Requirements Model

The leadership requirements model identifies core competencies and attributes applicable to all types and echelons of Army organizations. The model conveys expectations and establishes the capabilities needed of all Army leaders regardless of rank, grade, uniform, or attire.
Human Advantage

A human advantage occurs when a force holds the initiative in terms of training, morale, perception, and will. Human advantages enable friendly morale and will, degrade enemy morale and will, and influence popular support.
Leadership

Leadership is the activity of influencing people by providing purpose, direction, and motivation to accomplish the mission and improve the organization. Leadership as an element of combat power, coupled with information, unifies the warfighting functions (movement and maneuver, intelligence, fires, sustainment, protection and command and control)...
Leadership as a Dynamic of Combat Power

Leadership is the most essential dynamic of combat power. Leadership is the activity of influencing people by providing purpose, direction, and motivation to accomplish the mission and improve the organization. It is the multiplying and unifying dynamic of combat power, and it represents the qualitative difference between units.
8-Step Training Model

Training models are an effective technique for small units (company and below) to plan and prepare a training event. They provide a logical and reliable framework of activities and actions for small-unit leaders to plan and prepare, execute, and evaluate single training events. The 8-step training model is the Army’s preeminent training model.
T-Week Calendar

Training events can be managed using the T-Week calendar framework. This is a planning technique that identifies actions and activities to accomplish prior to each training event. T-Week is the week of training execution; T-6 represents activities six weeks prior to execution.
“P Week” System

The “P Week” System is an alternative time management system to the “Green-Amber-Red” time management system...
“Green-Amber-Red” Time Management System

Commanders prioritize training time by utilizing a time management system. The most common time management system used within the Army is the Green-Amber-Red cycle...
Training Management Cycle

The training management cycle is the process of prioritizing training, planning and preparation, execution, and the evaluation and assessment of training.
Principles of Training

The principles of training provide foundational direction for all commanders and leaders. These principles guide and influence training at every echelon.
NEW! TLS7: The Leader’s SMARTbook, 7th Ed.

TLS7: The Leader’s SMARTbook, 7th Ed. is the seventh edition of The Leader’s SMARTbook, completely updated for 2023. TLS7 focuses on gaining the human advantage and leadership as a dynamic of combat power (FM 3-0, 2022), developing leaders, and training, the most important thing the Army does to prepare for operations...
The Middle East (Forces, Conflicts, and Threats)
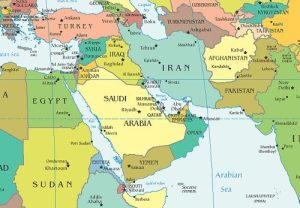
Spanning more than 4.6 million square miles, the Middle East has for millennia been a geographic and geopolitical crossroads and site of cooperation, competition, and conflict. Rich in cultural heritage but with unevenly distributed natural resources, the region is also beset by internal conflict and instability...
CENTCOM Strategic Priorities: Deter, Counter, Compete

As identified in the Statement of General Michael “Erik” Kurilla on the Posture of U.S. Central Command - SASC Hearing Mar 16, 2023, Central Command's (CENTCOM) strategic priorities are: deter Iran, counter violent extremist organizations, and to compete strategically...
Iranian Threat

The greatest single day-to-day threat to regional security and stability in the Middle East remains Iran, which challenges the U.S. and its allies by pursuing regional hegemony, breaching its JCPOA commitments, and posing a conventional threat to partner nations while facilitating and conducting coercive and malign activities...
NEW! OPFOR SMARTbook 4 – Iran & the Middle East

The greatest single day-to-day threat to Middle East regional security and stability remains Iran, which challenges the U.S. and its allies by pursuing regional hegemony, breaching its JCPOA commitments, and posing a conventional threat to partner nations...
NEW! Joint/Interagency SMARTbook 1 – Joint Strategic & Operational Planning, 3rd Ed.

JIA1-3 is the new third edition of our Joint/Interagency SMARTbook 1: Joint Strategic & Operational Planning (Planning for Planners), completely reorganized and updated with the latest joint publications for 2023 to include JP 3-0 Joint Campaigns and Operations (2022) and JP 5-0 Joint Planning (2020). At 420-pgs, JIA1-3 is designed to give the reader a thorough understanding of the joint planning and execution process, where the joint planning process (JPP) resides...
Combat Power
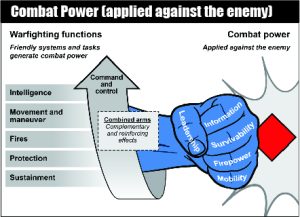
Combat power is the total means of destructive and disruptive force that a military unit/formation can apply against an enemy at a given time (JP 3-0). It is the ability to fight. The complementary and reinforcing effects that result from synchronized operations yield a powerful blow that overwhelms enemy forces and creates friendly momentum. Army forces deliver that blow through a combination of five dynamics...
NEW! AODS7: The Army Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook, 7th Ed.

AODS7: The Army Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook, 7th Ed. (Multidomain Operations) is completely updated with the 2022 edition of FM 3-0. AODS7 focuses on Multidomain Operations and features rescoped chapters on generating and applying combat power: command & control (ADP 6-0), movement and maneuver (ADPs 3-90, 3-07, 3-28, 3-05), intelligence (ADP 2-0), fires (ADP 3-19), sustainment (ADP 4-0), & protection (ADP 3-37).
NEW! OPFOR SMARTbook 2 – North Korean Military

North Korea is one of the most militarized countries in the world and remains a critical security challenge for the United States, our Northeast Asian allies, and the international community...
NEW! OPFOR SMARTbook 1 – Chinese Military

For over two thousand years, China has been surrounded by enemies, adversaries, and other competitors. Invasion, occupation, raids, and other incursions into Chinese territory were commonplace. ..
NEW! OPFOR SMARTbook 5 – Irregular & Hybrid Threat

A hybrid threat is the diverse and dynamic combination of regular forces, irregular forces, and/or criminal elements all unified to achieve mutually benefitting effects. Irregular forces are armed individuals or groups who are not members of the regular armed forces, police, or other internal security forces...
PODCAST: SMARTbooks in the News!

Listen to SMARTbook Author and Publisher Norman M. Wade talk with host Dr. Thomas Withington about the CYBER1 SMARTbook and other military reference SMARTbooks as a guest on the Armada Analysis's Electronic Warfare Podcast...
Leveraging Information (in Military Operations)

All military activities produce information. The joint force commander (JFC) leverages informational aspects of military activities to gain an advantage; failing to leverage those aspects may cede this advantage to others. Leveraging the informational aspects of military activities ultimately affects strategic outcomes...
Information Joint Function

All military activities have an informational aspect since most military activities are observable in the Information Environment (IE). Informational aspects are the features and details of military activities observers interpret and use to assign meaning and gain understanding. Those aspects affect the perceptions and attitudes that drive behavior and decision making. The JFC leverages informational aspects of military activities to gain an advantage in the OE; failing to leverage those aspects in a timely manner may cede this advantage to an adversary or enemy.
Information (as Dynamic of Combat Power)

Combat power is the total means of destructive and disruptive force that a military unit/formation can apply against an enemy at a given time (JP 3-0). As a dynamic of combat power, Army forces fight for, defend, and fight with information.
Information-Related Capabilities (IRCs)

An information-related capability (IRC) is a tool, technique, or activity employed within a dimension of the information environment that can be used to create effects and operationally desirable conditions (JP 1-02). Information Operations (IO) brings together information-related capabilities (IRCs) at a specific time and in a coherent fashion to create effects in and through the information environment that advance the ability to deliver operational advantage to the commander...
Information Environment

The Army’s model of an operational environment (OE) established in FM 3-0 no longer includes an information environment. The term informational considerations is similar to the joint term and definition of information environment...
Information Operations (IO) – Defined & Described

Information Operations (IO) is the integrated employment, during military operations, of information-related capabilities in concert with other lines of operation to influence, disrupt, corrupt, or usurp the decision-making of adversaries and potential adversaries while protecting our own (JP 3-13)...
NEW! INFO1: The Information Operations & Capabilities SMARTbook

Over the past two decades, information operations (IO) has gone through a number of doctrinal evolutions, explained, in part, by the rapidly changing nature of information, its flow, processing, dissemination, impact and, in particular, its military employment...
NEW! SMFLS5: The Sustainment & Multifunctional Logistics SMARTbook, 5th Ed.

SMFLS5:The Sustainment & Multifunctional Logistics SMARTbook, 5th Ed. has been completely updated for 2021. At 368 pages, SMFLS5 topics and references include...
Elements of Sustainment

The sustainment warfighting function consists of four elements: logistics, financial management, personnel services and health service support as shown in the sustainment warfighting function logic chart.
Marine Corps Planning Process (MCPP)
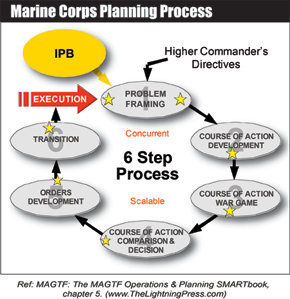
The Marine Corps Planning Process (MCPP) is a six-step process to understand the situation and mission, develop a COA, and produce an plan...
R2P2 – Rapid Response Planning Process
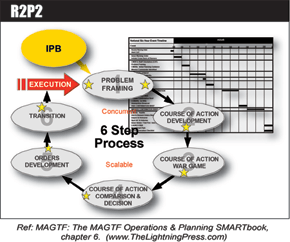
The Rapid Response Planning Process (R2P2) is an accelerated execution of MCPP geared to Crisis Action Planning. R2P2 allows the MEU/PHIBRON...
Intelligence Preparation of the Battlespace (IPB)

Intelligence Preparation of the Battlespace is the Marine Corps-specific version of IPB related to the Marine Corps Planning Process (MCPP), with Marine Corps terminology and phrasing, whereas "Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield" is the U.S. Army version...
NEW! The MAGTF Operations & Planning SMARTbook

The MAGTF Operations & Planning SMARTbook by Andrew Milburn and Norman M. Wade topics and chapters include Marine Corps roles & forces, the Marine Air-Ground Task Force (MAGTF), expeditionary operations, Marine Corps operations...
NEW! MEU3: The Marine Expeditionary Unit SMARTbook, 3rd Ed.

The Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU) SMARTbook is designed to be a reference for MEU and PHIBRON Commanders, MEU and PHIBRON staffs and the commanders and staffs of the Major Subordinate Elements (MSE) and Naval Support Elements (NSE) of the ARG-MEU team...
NEW! AODS6-1: The Army Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook, 6th Ed. (w/SMARTupdate 1)

AODS6-1: The Army Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook (w/SMARTupdate 1) is the new sixth edition of our Army SMARTbook. In addition to operations (ADP 3-0) and large-scale combat operations (FM 3-0), the 400-pg AODS6 includes...
NEW! The Small Unit Tactics SMARTbook, 3rd Ed. (SUTS3)

SUTS3: The Small Unit Tactics SMARTbook, 3rd Ed. is the third revised edition of The Small Unit Tactics SMARTbook, completely updated for 2019 to include ADP 3-90 Offense and Defense (Aug ‘18), FM 3-0 Operations (Oct ‘17), FMs 3-90-1 & -2 (May ‘13), ATP 3-21.8 Infantry Platoon and Squad (Apr ‘16), ATP 3-21.10 Infantry Rifle Company (May ‘18), TC 3-21-76 The Ranger Handbook (Apr ‘17), and the latest versions of more than 20 additional references.
Electronic Warfare (EW) Operations
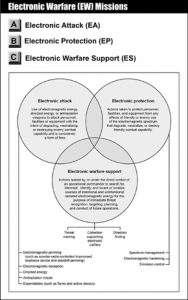
Electronic warfare refers to military action involving the use of electromagnetic and directed energy to control the electromagnetic spectrum or to attack the enemy (JP 3-13.1).
Cyberspace Operations
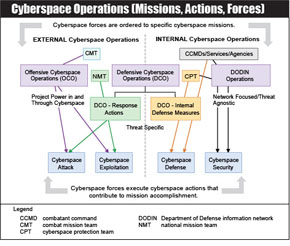
Cyberspace Operations (CO) are the employment of cyberspace capabilities where the primary purpose is to achieve objectives in or through cyberspace. CO comprise the military, national intelligence, and ordinary business operations of DOD in and through cyberspace. CCDRs and Services use CO to create effects in and through cyberspace in support of military objectives.
Electromagnetic Spectrum (EMS)
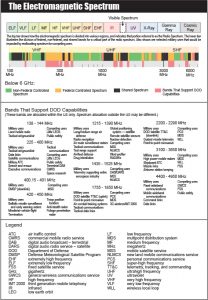
The electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation from zero to infinity. It is divided into 26 alphabetically designated bands. Military operations are complicated by increasingly complex demands on the EMS.
Cyberspace
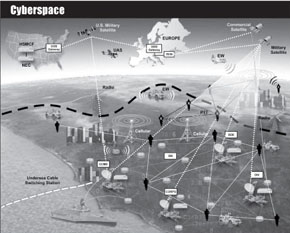
Cyberspace is a global domain within the information environment consisting of the interdependent networks of information technology infrastructures and resident data, including the Internet, telecommunications networks, computer systems, and embedded processors and controllers.
NEW! CYBER1: The Cyberspace Operations & Electronic Warfare SMARTbook

United States armed forces operate in an increasingly network-based world. The proliferation of information technologies is changing the way humans interact with each other and their environment, including interactions during military operations.
Russian Military Principles & Foundations

To the Soviets, war was a manifestation of the class struggle. It was an expression of the conflict between the “progressive forces of socialism” and the “reactionary forces of imperialistic capitalism"...
FM 100-2 Series – Opposing Forces and the Historical Soviet Threat Model

The Soviet threat was described in great detail in the 80s with the FM 100-2 series. The three-volume set was the definitive source of unclassifed information on Soviet ground forces and the Soviet model of combined arms warfare. The series is now out-of-print and largely unavailable...
NEW 2nd Edition! OPFOR SMARTbook 3 – Red Team Army (OPFOR3-2)

In today’s complicated and uncertain world, it is impossible to predict the exact nature of future conflict that might involve U.S. forces...
National Incident Management System (NIMS)
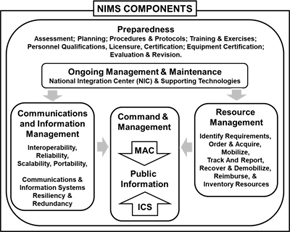
NIMS guides all levels of government, nongovernmental organizations (NGO), and the private sector to work together to prevent, protect against, mitigate, respond to, and recover from incidents. NIMS provides stakeholders across the whole community with the shared vocabulary, systems, and processes to successfully deliver the capabilities described in the National Preparedness System.
New! Disaster Response SMARTbook 1 – Federal/National Disaster Response

As a Nation we must maintain a state of readiness to respond to both natural disasters and man-made threats. At the National level, these efforts reflect consideration of both disaster response and national security requirements.
Joint Intelligence Preparation of the Operational Environment (JIPOE)
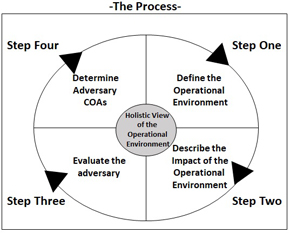
Joint Intelligence Preparation of the Operational Environment (JIPOE) is the analytical process used by joint intelligence organizations to produce intelligence assessments, estimates, and other intelligence products in support of the commander’s decision-making process.
Joint Planning Process (JPP)
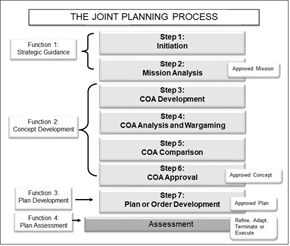
The Joint Planning Process (JPP) is an orderly, analytical process, which consists of a set of logical steps to examine a mission; develop, analyze, and compare alternative COAs; select the best COA; and produce a plan or order...
Global Force Management (GFM)
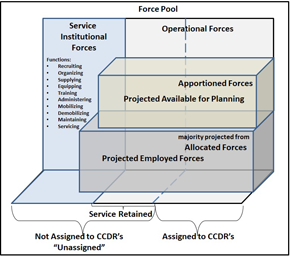
Global Force Management (GFM) directs the Services to provide sufficient ready and available forces to execute the National Defense Strategy...
Joint Operation Planning Process for Air (JOPPA)
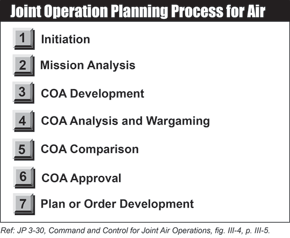
The JFACC is responsible for planning joint air operations and uses the joint operation planning process for air (JOPPA) to develop a JAOP that guides employment of the air capabilities and forces made available to accomplish missions assigned by the JFC.
Joint Air Operations Planning

The JFACC’s role is to plan joint air operations. In doing so, the JFACC provides focus and guidance to the JAOC staff. The JFACC uses the entire staff during planning to explore the full range of adversary and friendly COAs...
NEW! AFOPS2: The Air Force Operations & Planning SMARTbook, 2nd Ed.

AFOPS2: The Air Force Operations & Planning SMARTbook, 2nd Ed. (Guide to Curtis E. LeMay Center & Joint Air Operations Doctrine) is the second edition...
Large-Scale Combat Operations

Large-scale combat operations are intense, lethal, and brutal. Their conditions include complexity, chaos, fear, violence, fatigue, and uncertainty. Future battlefields will include noncombatants, and they will be crowded in and around large cities.
Conflict Continuum
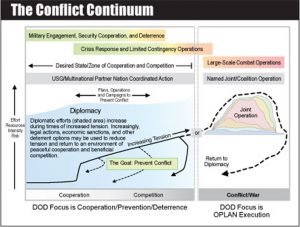
Threats to US and allied interests throughout the world can sometimes only be countered by US forces able to respond to a wide variety of challenges along a conflict continuum that spans from peace to war...
Range of Military Operations
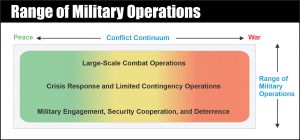
The range of military operations is a fundamental construct that helps relate military activities and operations in scope and purpose. The potential range of military activities and operations extends from military engagement, security cooperation, and deterrence in times of relative peace up through large-scale combat operations.
Close Combat

Close combat is indispensable and unique to land operations. Only on land do combatants routinely and in large numbers come face-to-face with one another. When other means fail to drive enemy forces from their positions, Army forces close with and destroy or capture them. The outcome of battles and engagements depends on Army forces’ ability to prevail in close combat...
Joint Planning

Joint planning consists of planning activities associated with joint military operations by combatant commanders (CCDRs) and their subordinate joint force commanders (JFCs) in response to contingencies and crises. It transforms national strategic objectives into...
NEW! JFODS5: The Joint Forces Operations & Doctrine SMARTbook, 5th Ed.

Achieving national strategic objectives requires effective unified action resulting in unity of effort -- to include interagency, intergovernmental, nongovernmental and multinational partners....
Small Unit Tactics

Tactics is the employment and ordered arrangement of forces in relation to each other. Through tactics, commanders use combat power to accomplish missions. The tactical-level commander uses combat power in battles, engagements, and small-unit actions...
The Operations Process
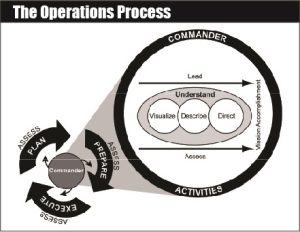
The Army’s framework for exercising mission command is the operations process--the major mission command activities performed during operations: planning, preparing, executing, and continuously assessing the operation. Commanders, supported by their staffs, use the operations process to...
Joint Operations
The primary way the Department of Defense (DOD) employs two or more Services (from at least two Military Departments) in a single operation is through joint operations. Joint operations are military actions conducted by joint forces and those Service forces employed in specified command relationships with each other, which of themselves do not establish joint forces...
Maneuver Enhancement Brigade (MEB)
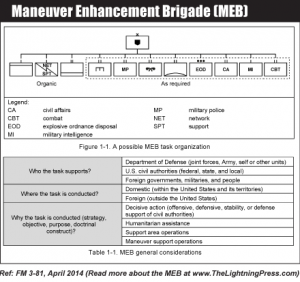
The Maneuver Enhancement Brigade (MEB) is a unique, multifunctional, mission command headquarters that is organized to perform support area operations for the echelon that it supports...
Military Deception

Military deception is both a process and a capability. As a process, military deception is a methodical, information-based strategy that systematically, deliberately, and cognitively targets individual decisionmakers.
Mission Command
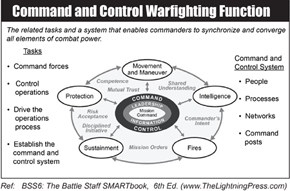
Mission command is the Army’s approach to command and control that empowers subordinate decision making and decentralized execution appropriate to the situation. Mission command supports the Army’s operational concept of unified land operations and its emphasis on seizing, retaining, and exploiting the initiative.
Critical Infrastructure Protection
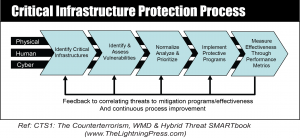
Critical infrastructure protection (CIP) is a concept that relates to the preparedness and response to serious incidents that involve the critical infrastructure of a region or nation...
Train, Advise and Assist

The recent announcement of “Advisory Brigades” by Army Chief of Staff Gen. Mark A. Milley focuses on the need for specialized units to train and advise foreign forces. Called train, advise and assist brigades, the units would deploy to different combatant command areas to help train allies and partners, similar to what units have been doing in Iraq and Afghanistan...
NEW! TAA2: The Military Engagement, Security Cooperation & Stability SMARTbook, 2nd Ed. (w/Change 1)

TAA2: The Military Engagement, Security Cooperation & Stability SMARTbook is the re-titled and re-focused second edition of The Stability, Peace & Counterinsurgency SMARTbook...
The Art and Science of Tactics

The tactician must understand and master the science and the art of tactics, two distinctly different yet inseparable concepts. Commanders and leaders at all echelons and supporting commissioned, warrant, and noncommissioned staff officers must be tacticians to lead their soldiers in the conduct of full spectrum operations...
Domestic Terrorism

Domestic terrorism involves groups or individuals who are based and operate entirely within the United States or its territories without foreign direction and whose acts are directed at elements of the U.S. Government or population.
Combating Terrorism Center at West Point
The Combating Terrorism Center is an independent, privately funded, research and educational institution situated at West Point that contributes to the academic body of knowledge and informs counterterrorism policy and strategy.
Sustainment Warfighting Function

The sustainment warfighting function is related tasks and systems that provide support and services to ensure freedom of action, extend operational reach, and prolong endurance (ADP 3-0).
Forms of Terrorism

Forms of terrorism threats range from non-state transnational networks with global reach capability such as al-Qaida, terrorist cells affiliated with regional or international aims, or individual self-radicalized and unaffiliated terrorists with single issue agendas.
NEW! CTS1: The Counterterrorism, WMD & Hybrid Threat SMARTbook

Terrorism has evolved as a preferred tactic for ideological extremists around the world, directly or indirectly affecting millions of people. Terrorists use many forms of unlawful violence or threats of violence...
NEW! MEU2: The Marine Expeditionary Unit SMARTbook, 2nd Ed.

The Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU) SMARTbook is designed to be a reference for MEU and PHIBRON Commanders, MEU and PHIBRON staffs and...
Army Values

The list of Army Values are Loyalty, Duty, Respect, Selfless Service, Honor, Integrity, and Personal Courage, which comprise the acronym LDRSHIP.
Urban Operations

Urban areas present the most complex environment for military operations. Commanders conducting major urban operations use their ability to visualize how doctrine and military capabilities are applied within the context of the urban environment.
Elements of a Combat Patrol

There are three essential elements for a combat patrol: security; support; and assault. The size of each element is based on the situation and the analysis of METT-TC.
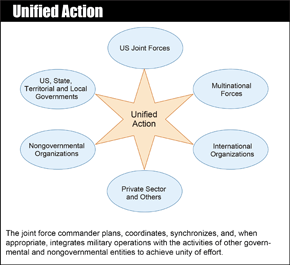
Unified Action

Unified action refers to the synchronization, coordination, and integration of the activities of governmental and nongovernmental entities to achieve unity of effort. Failure to achieve unity of effort can cost lives, create conditions that enhance instability, and jeopardize mission accomplishment.
Special Purpose Attacks

Special purpose attacks are ambush, spoiling attack, counterattack, raid, feint, and demonstration. The commander’s intent and the factors of METT-TC determine which of these forms of attack are employed.
NEW! The Sustainment & Multifunctional Logistics SMARTbook, 4th Ed. (SMFLS4)

The sustainment warfighting function is related tasks and systems that provide support and services to ensure freedom of action, extend operational reach, and prolong endurance...
Unit Training Plans (UTP)

The unit training plan (UTP) uses a crawl-walk-run approach that progressively and systematically builds on successful task performance before progressing to more complex tasks.
Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB)

Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB) is the systematic process of analyzing the mission variables of enemy, terrain, weather, and civil considerations in an area of interest to determine their effect on operations.
Adaptive Planning and Execution (APEX)
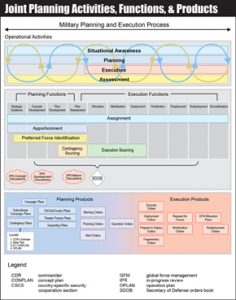
Joint operation planning occurs within Adaptive Planning and Execution (APEX), which is the department-level system of joint policies, processes, procedures, and reporting structures.
Raid
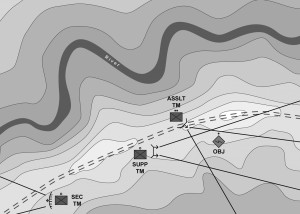
A raid is an operation to temporarily seize an area in order to secure information, confuse an adversary, capture personnel or equipment, or to destroy a capability culminating with a planned withdrawal.
Defense Support to Civil Authorities (DSCA)
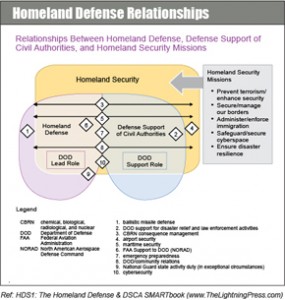
Defense Support of Civil Authorities (DSCA) is support in response to a request for assistance from civil authorities for domestic emergencies...
Incident Command System Courses
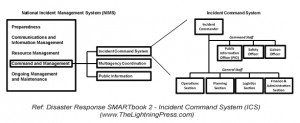
The Incident Command System (ICS) SMARTbook provides a detailed explanation of ICS as outlined in FEMA Emergency Management courses 100, 200, 300, 400, 700, 703, and 800; including 2015 updates.
Ambush Categories
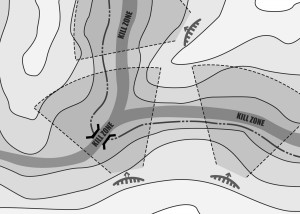
Ambushes are classified by category (deliberate or hasty), formation (linear or L-shaped), and type (point, area, or antiarmor). The leader determines the category of ambush through an analysis of the factors of METT-TC.
Incident Command System Training

The Incident Command System (ICS) SMARTbook provides an outline of FEMA Emergency Management courses 100, 200, 300, 400, 700, 703, and 800; including 2015 updates and provides a ready resource for reference and training.
About the Military Decision-Making Process (MDMP)
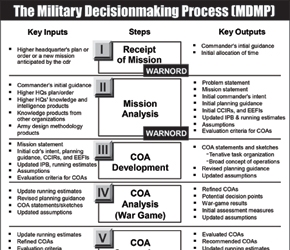
The Military Decisionmaking Process (MDMP) consists of seven steps. Each step of the MDMP has various inputs, a method (step) to conduct, and outputs...
Joint Planning and Execution Community (JPEC)
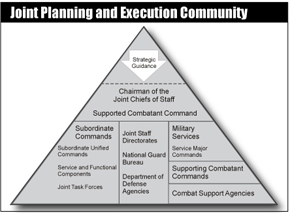
The headquarters, commands, and agencies involved in joint operation planning or committed to a joint operation are collectively termed the Joint Planning and Execution Community (JPEC)...
Ambush
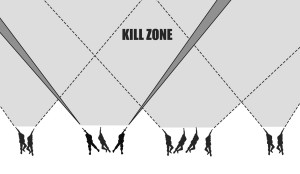
An ambush is an attack by fire or other destructive means from concealed positions on a moving or temporarily halted enemy. It may take the form of an assault to close with and destroy the enemy, or be an attack by fire only.
Homeland Defense (HD)

Homeland Defense (HD) is the protection of US sovereignty, territory, domestic population, & critical infrastructure against external threats & aggression...
Incident Command System (ICS)

Disaster can strike anytime, anywhere. The Incident Command System (ICS) helps ensure integration of our response efforts. ICS is a standardized, on-scene, all-hazards approach to incident management.
Joint Strategic Planning System (JSPS)
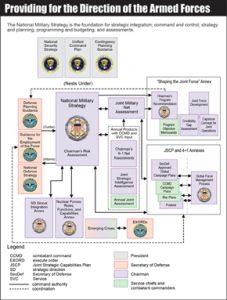
Joint Strategic Planning System (JSPS) is the primary system by which the JCS and the CCDRs conduct deliberate planning and provides military advice to the President and SecDef...
Far Ambush

The far ambush has only the purpose of injuring and/or delaying the target. This rarely ever calls for an assaulting force—since the patrol doesn’t seek the complete destruction of the enemy force there is no need to risk the loss of friendly troops. The far ambush simply intends to harass.
NEW! Disaster Response SMARTbook 2: Incident Command System (DRS2)

Disaster can strike anytime, anywhere. The Incident Command System (ICS) helps ensure integration of our response efforts. ICS is a standardized, on-scene...
Joint Interagency Coordination Group (JIACG)
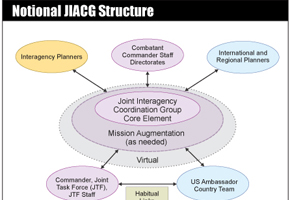
A Joint Interagency Coordination Group (JIACG) is an interagency staff group that establishes regular, timely, and collaborative working relationships....
Near Ambush

The near ambush has the expressed purpose of destroying the target. This often requires an assaulting force to literally overrun the target after the initial volley of fire has inflicted tremendous damage.
Joint Operation Planning

Joint operation planning consists of planning activities associated with joint military operations by combatant commanders (CCDRs) and...
About the Warfighting Functions

Commanders use the warfighting functions to help them exercise command and...
Military Decision-Making Process (MDMP)

The Military Decision Making Process (MDMP) consists of seven steps. Each step of the MDMP has various inputs, a method (step) to conduct, and outputs...
NEW! The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 5th Ed. (BSS5)

Commanders, supported by their staffs, use the operations process to drive the conceptual and detailed planning necessary to understand, visualize, and describe their operational environment; make and articulate decisions; and direct, lead, and assess military operations...
Homeland Security

Homeland Security (HS) is a concerted national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the US; reduce domestic vulnerability to terrorism, major disasters, and other emergencies...
Patrols & Patrolling

A patrol is sent out by a larger unit to conduct a specific combat, reconnaissance, or security mission. A patrol’s organization is temporary and specifically matched to the immediate task.
NEW! Cultural Guide SMARTbook 1: Afghanistan

Cultural awareness has become an increasingly important competency for leaders at all levels. Perceptive leaders learn how cultures affect operations...
Unit Training Management (UTM)

Unit Training Management (UTM) provides the key how-to details of the US Army’s training processes that bridge the doctrine and the dynamic tools (ATN/CATS/DTMS/HQ DA Standardized METL) to make planning, preparing, executing and assessing unit training possible.
Joint Interagency Task Force (JIATF)

A Joint Interagency Task Force (JIATF) may be formed when the mission requires close integration of two or more USG agencies...
NEW! The Homeland Defense & DSCA SMARTbook (HDS1)

Homeland Defense is the protection of US sovereignty, territory, domestic population, critical infrastructure or other threats as directed by the President...
About the Elements of Combat Power
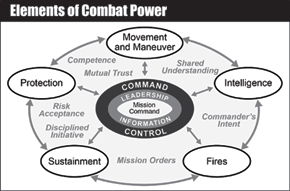
To execute operations, commanders conceptualize capabilities in terms of combat power...
NEW! Disaster Response SMARTbook 3: Disaster Preparedness (DRS3)

Surviving Disasters on Your Own Terms. Sometimes things go badly and all our hopes and plans fail us. Our illusions are shattered, our expectations are beyond anyone’s capacity to fulfill, and our demands go unanswered...
SMARTleaders at the University of Virginia ROTC!

ROTC Cadets at the University of Virginia with their SMARTleader book donations from The Lightning Press...
Patrol Organization

A patrol is organized to perform specific tasks. It must be prepared to secure itself, navigate accurately, identify and cross danger areas, and reconnoiter the patrol objective.
About the Elements of Decisive Action
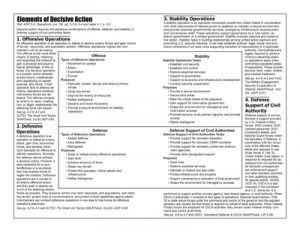
Army forces demonstrate the Army’s core competencies through decisive action—the continuous, simultaneous...
Understanding the Instruments of National Power

National power is defined as the sum of all resources available to a nation in the pursuit of national objectives. The phrase instruments of national power refers to the tools a country uses to influence other countries or international organizations or even non-state actors....







