The rapid decision-making and synchronization process (RDSP) is a technique that commanders and their staffs commonly use during execution. While identified here with a specific name and method, the approach is not new; its use in the Army is well established and tested. When using this technique:
While the military decision-making process (MDMP) seeks the optimal solution, the RDSP seeks a timely and effective solution within the commander’s intent. Using the RDSP lets leaders avoid the time-consuming requirements of developing decision criteria and comparing COAs. Under the RDSP, leaders combine their experience and intuition to quickly reach situational understanding.
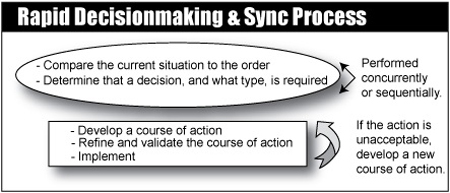
Based on this, they develop and refine acceptable COAs. The RDSP facilitates continuously integrating and synchronizing the warfighting functions to address ever-changing situations. It meets the following criteria for making effective decisions during execution:
A. Compare the Current Situation to the Order
Commanders and staffs identify likely variances during planning and identify potential options and actions that will likely be available when each variance occurs. During execution, commanders and staffs monitor the situation to identify changes in conditions. They then identify if the changed conditions represent variances from the order—especially opportunities, threats, and risks they present. Staff members use running estimates to look for indicators of variances that affect their areas of expertise.
B. Determine the Decision Required
When a variance is identified, the commander directs action while the chief of operations leads the current operations integration cell and selected functional cells in quickly comparing the current situation to the expected situation.
C. Develop a Course of Action
If the variance requires an adjustment decision, the designated integrating cell and affected command post cell chiefs recommend implementation of a COA or obtain the commander’s guidance for developing one. They use the following conditions to develop possible COAs:
D. Refine and Validate the Course of Action
Once commanders describe the new COA, the current operations integration cell conducts an analysis to validate its feasibility, suitability, and acceptability. If acceptable, the COA is refined to resynchronize the warfighting functions enough to generate and apply the needed combat power. Staffs with a future operations cell may assign that cell responsibility for developing the details of the new COA and drafting a FRAGORD to implement it. The commander, COS, or XO may direct a hasty operations synchronization meeting to perform this task and ensure rapid resynchronization.
E. Implement
When a COA is acceptable, the COS or XO recommends implementation to the commander or implements it directly, if the commander has delegated that authority. Implementation normally requires a FRAGORD; in exceptional circumstances, it may require a new operation order (OPORD). That order changes the concept of operations (in adjustment decisions), resynchronizes the warfighting functions, and disseminates changes to control measures. The staff uses warning orders (WARNORDs) to alert subordinates to a pending change. The staff also establishes sufficient time for the unit to implement the change without losing integration or being exposed to unnecessary tactical risk.
Editor’s note: Army leaders employ several methodologies for planning, determining the appropriate mix based on the scope and understanding of the problem, time available, and availability of a staff. Army planning methodologies include the Army design methodology (ADM), military decisionmaking process (MDMP), troop leading procedures (TLP), rapid decision-making and synchronization process (RDSP), and Army problem solving. All five planning methodologies are discussed in The Battle Staff SMARTbook.
 This article is an extract from "BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed. (Planning & Conducting Multidomain Operations)" by The Lightning Press. Download a free PDF sample and learn more at: BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed. (Planning & Conducting Multidomain Operations).
This article is an extract from "BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed. (Planning & Conducting Multidomain Operations)" by The Lightning Press. Download a free PDF sample and learn more at: BSS7: The Battle Staff SMARTbook, 7th Ed. (Planning & Conducting Multidomain Operations).
Browse additional military doctrine articles in our SMARTnews Blog & Resource Center.
About The Lightning Press SMARTbooks. Recognized as a “whole of government” doctrinal reference standard by military, national security and government professionals around the world, SMARTbooks comprise a comprehensive professional library. SMARTbooks can be used as quick reference guides during operations, as study guides at education and professional development courses, and as lesson plans and checklists in support of training. Browse our collection of Military Reference SMARTbooks to learn more.













































